Biography
 |
| Hüseyin Kaya |
| hkayabilisim@gmail.com |
Hüseyin Kaya graduated from Middle East Technical University in 2000 with a bachelor’s degree in Mathematics. He completed his master’s degree in Computational Science and Engineering program of Istanbul Technical University. During the thesis, he worked as a research assistant and system administrator at the Informatics Institute of the same university. After graduation, he began working in Iontek Inc., one of the first bioinformatics companies in Turkey, as a software developer and project manager.
The development of a new time series classifier in one of the mutation analyses projects of the company became the starting point of his doctoral dissertation which he successfully completed in Istanbul Technical University. In the meantime, he was employed as a full-time Linux System Administrator in Asseco South Eastern Europe, an e-commerce company. He completed his one-year post-doctoral study with Prof. Robert. D. Skeel at Purdue University, focusing on the development of new fast summation methods aimed to reduce the computational costs of n-body algorithms. Upon returning to Turkey, he worked briefly at Kadir Has University on Fall 2017 and later joined Payten as a Senior Solution Architect. He is currently leading the company’s R&D projects and supervising a consortium in building a new auto-scaler targeted to cloud applications.
Education
- Ph.D. - Istanbul Technical University, Computational Science and Engineering, “Time Series Classification Based on the Genetic Algorithm and Smooth Monotone Increasing Functions”, 2014.
- M.Sc. - Istanbul Technical University, Computational Science and Engineering, “Using Direct Methods for Solution of Neutron Diffusion Equation”, 2003.
- B.Sc. - Middle East Technical University, Mathematics, 2000.
Selected Publications
Bulut Uygulamalarında Evrensel Duyarlılık Analizi (Turkish)
Hüseyin Kaya
Türkiye Bilişim Vakfı Bilgisayar Bilimleri ve Mühendisliği Dergisi 15.1 (2022): 77-84.
Dergi Park,
GitHub,
ResearchGate,
Google Scholar
This is a Turkish publication about measuring sensitivity of cloud application parameters. As an application we've chosen a benchmark microservice application named TeaStore. For the set of parameters, we selected three parameters each represent a different aspect of application management: horizontal scaling, vertical scaling and performance tuning. To measure the sensitivity, High Dimensional Model Representation is used.
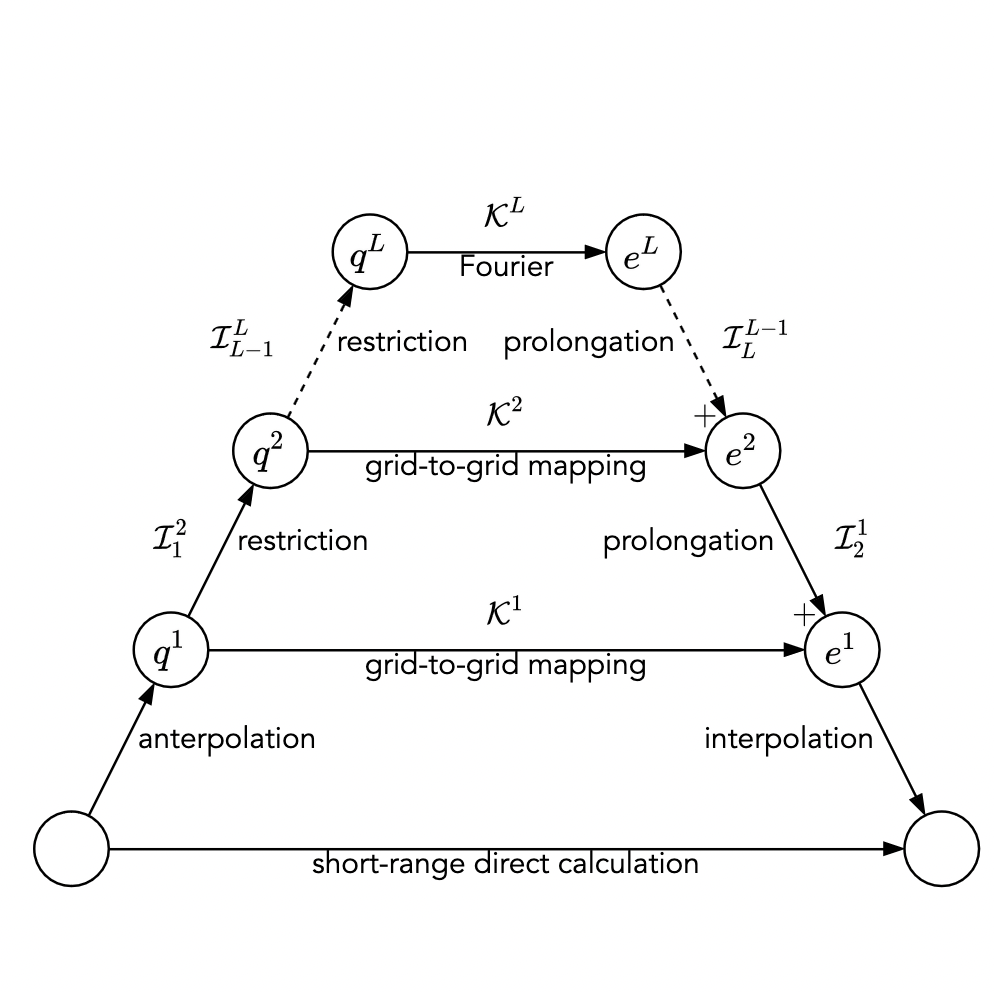
Multilevel summation for periodic electrostatics using B-splines
Hüseyin Kaya, David J. Hardy, and Robert D. Skeel
The Journal of Chemical Physics 154.14 (2021)
Code Ocean,
GitHub,
AIP,
ResearchGate,
Google Scholar
This manuscript is the result of a long research process about implementing B-splines in multilevel summation method which was my main research topic when I was a visiting researcher at Purdue University. Multilevel summation is a fast summation method usually used in speeding up molecular dynamics simulations. I've chosen this topic for my post-doc because I was familiar with the concept as I had already attempted to develop a new fast summation method for gravitational n-body problems in 2005. It was a great privilage to work with Professor Skeel and I've learned a lot from him. After this publication, our next target was to apply our method to gravitation and esspecially cosmology simulations. I'm planning to come back to this study and finish my dream as a tribute to Professor Skeel.

Feature selection based on high dimensional model representation for hyperspectral images
Gülşen Taşkın, Hüseyin Kaya, and Lorenzo Bruzzone
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 26.6 (2017): 2918-2928
IEEE Xplore,
CodeOcean,
GitHub,
ResearchGate,
Google Scholar
This is the first study using the High Dimensional Model Representation (HDMR) as a feature selection algorithm. Suppose you have a supervised model for hyperspectral image classification and you want to determine which spectral channels are playing most important role in classification. Our idea is very simple: build a meta-model by using first-order HDMR. Then we calculate the Sobol indicies which are always positive and show the level of individual contribution of each spectral channels. This is nothing but feature selection.

Feature based quality assessment of DNA sequencing chromatograms
Ersoy Öz, Serkan Kurt, Musa Hakan Asyalı, Hüseyin Kaya and Yeliz Yücel
Applied Soft Computing 41 (2016): 420-427
ScienceDirect,
Web,
ResearchGate,
Google Scholar
DNA sequencing is a vital tool for diagnoising genetic disorders. The raw data generated during Sanger-based DNA sequencing is a four-channel timeseries which is further analysed to detect the nucleotide sequence. However, the accuracy of the generated sequence depends on the quality of the raw data. In this study, we developed a new approach to automatize the quality screening of DNA sequencing.
A distance based time series classification framework
Hüseyin Kaya, Şule Gündüz Öğüdücü
Information Systems 51 (2015): 27-42
ScienceDirect,
GitHub,
Web,
ResearchGate,
Google Scholar
This paper is one of the outcomes of my PhD thesis. I created a MATLAB program to combine the alignment and classification in one utility called Time Series Classification Utility (TSCU). It contains the alignment methods Dynamic Time Warping as well as Signal Alignment via Genetic Algorithm (SAGA) which I introduced in my thesis. TSCU also includes classification methods k-nearest neighbor and Support Vector Machines.
SAGA: A novel signal alignment method based on genetic algorithm
Hüseyin Kaya, Şule Gündüz Öğüdücü
Information Sciences 228 (2013): 113-130
ScienceDirect,
GitHub,
Web,
ResearchGate,
Google Scholar
SAGA stands for Signal Alignment based on Genetic Algorithm. As the name of the method suggests, we are using genetic algorithm for the purpose of alignment. SAGA is a direct result of my PhD study. In a few sentences, we describe the warping function between two time series via a differential equation first proposed by Ramsay and Silverman. The novelty is to determine the optimal parameters of the differential equation via Genetic Algorithm. The code is implemented in Time Series Classification Utility.
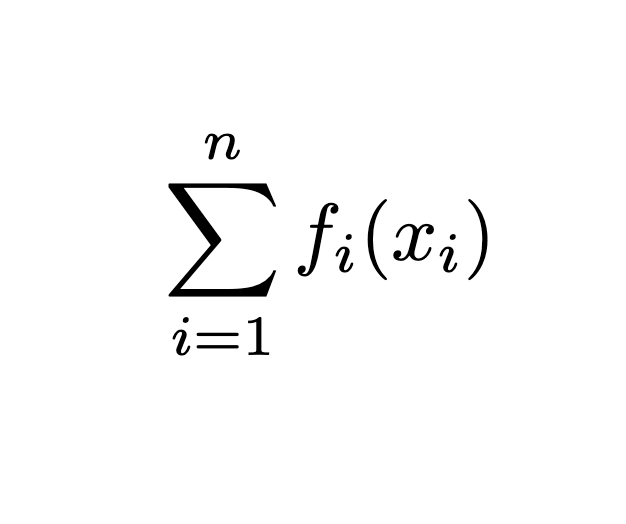
A recursive algorithm for finding HDMR terms for sensitivity analysis
Hüseyin Kaya, Murat Kaplan and Hasan Saygın
Computer Physics Communications 158.2 (2004): 106-112.
ScienceDirect,
ResearchGate,
Google Scholar
Calculating the HDMR components can be tricky and time consuming if the number of variables is large. Especially if the explicit form of the model is known, then the components are computed via taking integrations. To reduce the computation effort, we take advantage of cascading pattern in multiple integrations. All we need to do is to keep track of every integration step in a recursive manner so that there would be no redundant calculations.
Research Topics
My active research fields are:
- Machine learning/Artifical Intelligence
- Explainable Artificial Intelligence
- Meta-modelling techniques/High Dimensional Model Representation
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Computer Vision/Image Classification
And these are the topics I am also interested in and published papers about, but not actively involved right now:
- Time series alignment and classification
- Feature selection and sensitivity analysis
- Fast summation methods/multi-level summation
- Multifrontal methods for matrix solvers
- Neutron Diffusion Equation
- DNA sequence analysis/mutation detection
Projects

AI-based Auto-scaling and Tuning: APP2SCALE
Call: Eurostars-3 Call 2, funded by TÜBİTAK, CDTİ, Eureka and Horizon Europe
Date: Oct 2022 - Jan 2025
Consortium: Payten, Medianova, B2Metric, Turkcell, and Frizbit
Role: Project Manager
Development: GitHub
The history of this ongoing project goes back to 2019 when I was in pursuit of building a new scalable architecture for our payment gateway in Payten. I realized that the number of parameters involved in a scaling decision is so large that the best way is to escalate the task to an AI-based agent. We shared the idea with a few partners and quickly formed a consortium. After a long and tedius project preparation and evaluation process, our project has officially started on October, 2022.
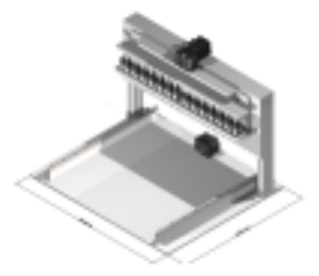
Automatic DNA Isolation Device with PCR Preparation Capability
Call: KOSGEB R&D Innovation Programme, funded by KOSGEB
Date: Oct 2011 - Oct 2012
Company: Iontek
Role: Project Manager
We designed a DNA isolation device capable of preparing 24-samples in parallel. The isolation robot also adds PCR reaction mixes so that the output samples can be directly used in PCR devices. At that time, there was a separte process to prepare PCR samples. Considering the pace of in-vitro devices in molecular biology, this machine is now obsolete. Nevertheless, it improved the competitive power of the company.